Recently, my friend shared a story about tech startups exploring a fascinating concept: reservoir computing. As artificial intelligence evolves, researchers and engineers search for innovative solutions to tackle predictive challenges. Among these solutions, reservoir computing stands out as a groundbreaking approach, capable of unraveling intricate patterns in data.
What is reservoir computing?
Reservoir computing (RC) is a machine learning method that uses a reservoir system, usually a recurrent neural network (RNN), to make predictions from sequential or time-series data.
How does it work?
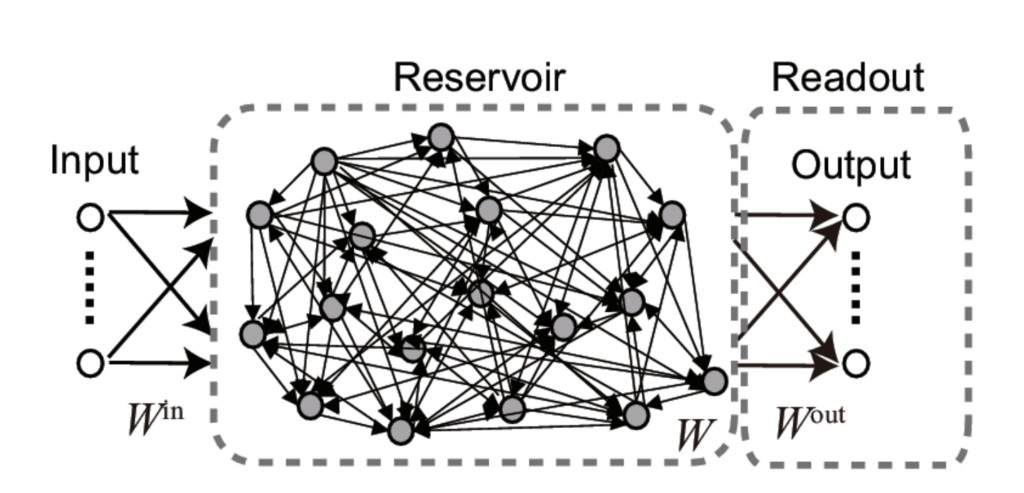
The three main parts of reservoir computing are:
- Input layer (data)
- Reservoir layer (randomly connected network)
- Output layer (readout layer): The output layer is the only trained part of reservoir computing and reads the reservoir activity to make predictions.
For instance, imagine you have a big fish tank (the “reservoir”) filled with many interconnected sensors.
- You pour in your data (like water) at one end.
- The data swirls around in the tank, interacting in complex ways.
- As it moves through the tank, the data gets transformed.
- At the other end, you have an output layer that reads the state of the water.
- This output layer learns to interpret the swirling patterns to solve problems or make predictions.
Nothing inside the tank changes, but the output layer in the end analyzes what the swirling means. The trainable output layer allows for pattern recognition or predicting what might happen next in a sequence of events.

What is this mysterious reservoir?
A reservoir is a fixed, untrained network of interconnected units, usually a recurrent neural network, that processes input data.
A reservoir must have two properties:
- It must be made up of individual, non-linear units.
- It must be able to store information.
Described as a “black box,” the internal dynamics of reservoirs often remain poorly understood and not thoroughly analyzed.
Reservoirs usually use a recurrent neural network, but can use other systems. A recurrent neural network (RNN) is a deep neural network trained on sequential data (like time series or sentences) to create a machine learning model. For instance, an RNN can predict daily flood levels based on past floods, tides, and meteorological data. RNN works best when context and order of data are crucial.
Pros of Reservoir Computing
The key advantage of reservoir computing (RC) includes fast learning capabilities and low training cost compared to other recurrent neural networks.
- Efficiency: RC increases efficiency because this method requires less training data to learn and generalizes better than traditional AI models.
- Reduces computational costs: RC performs training only at the readout stage, with fixed reservoir dynamics.
- Relatively simple framework to implement: RC utilizes basic computational units, and excels in handling complex systems, including those with chaotic and unpredictable behavior. RC often operates at the “edge of chaos,” a state that balances order and randomness, which is ideal for processing complex and chaotic data.
- Eliminates the need for hyperparameter optimization: RC allows for faster processing and adaptability to real-time data streams while maintaining low power consumption.
Cons of Reservoir Computing
- Long warm-up time: RC usually takes a longer warm-up time to make accurate predictions, which can be time-consuming.
- Performance is sensitive to hyperparameters: Hyperparameters such as reservoir size and weight matrix properties, may increase costs of creating the method.
- Highly sensitive: RC can be sensitive to small changes in input data.
- Significant amounts of labeled training data: RC usually needs labeled training data for optimal performance.
How can we use reservoir computing?
Reservoir computing can be used for complex data processing and time series analysis, such as radar signal classification and speech recognition. However, RC may also hold applications in the fashion, beauty, and wellness industries. In fashion, RC can forecast trends by analyzing historical data and consumer behavior patterns, optimize supply chain management through time-series data processing, and improve personalized recommendations based on individual customer preferences. In the beauty and wellness sector, RC can formulate effective skincare products by analyzing ingredient combinations over time and provide insights into purchasing patterns through customer interaction data.
Cover Photo: Hypebeast






Leave a comment